Abstract
Introduction: For patients (pts) with AML, a complete remission (CR) prior to allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (alloHCT) is a favourable risk factor. However, whether pts with relapsed or refractory (r/r) AML benefit from an attempt to induce CR with intensive chemotherapy (CT) prior to alloHCT is unknown. Sequential conditioning within 12 days prior to alloHCT with high-dose cytarabine or melphalan followed by reduced intensity conditioning leads to good results as well. Therefore, we asked whether intensive remission induction CT prior to alloHCT really improves outcome compared to immediate alloHCT after sequential conditioning without attempt to induce a CR before transplantation.
Methods: Adult pts with poor responsive non-favourable AML after first induction therapy (IT-1) or AML relapse, eligible for intensive CT and alloHCT, with either a matched sibling donor (MSD), an HLA-compatible (≥9/10) unrelated donor (UD) or ongoing donor search with two potential UD with ≥90% HLA-matching probability were enrolled. Patients were randomized 1:1 to a remission induction strategy (RIST-arm) with 3 g/m2 cytarabine (1 g/m2 for pts >60 years) twice daily on days 1-3 plus 10 mg/m2 mitoxantrone on days 3-5 (HAM) and subsequent alloHCT (remission induction strategy, RIST-arm) or to disease control (DISC-arm) prior to sequential conditioning and alloHCT. In the DISC-arm watchful waiting (w&w) was recommended, but low-dose cytarabine (LDAC) and single doses of mitoxantrone were permitted for disease-control. The primary endpoint was treatment success, defined as CR@day56 after alloHCT. Statistically, the goal was to show non-inferiority (NIF) for the DISC-arm with a NIF-margin of 5% and a one-sided alpha of 2.5%. Major secondary endpoints were overall survival from randomization and leukemia-free survival from CR@day56.
Results: A total number of 281 pts (183 pts with poor response after IT-1 and 98 pts after relapse) were enrolled. The full analysis set comprised 276 pts after exclusion of five pts due to violation of inclusion criteria. Median age was 61 years (interquartile range [IQR] 52-66 years) and the HCT-CI was ≥3 in 37.3% of pts. At randomization, 39 pts had MSD, 133 pts had an HLA-compatible UD with confirmed HLA-typing, and 104 pts had ongoing UD searches. 272 pts were treated per protocol, 138 pts in the DISC- and 134 in the RIST-arm.
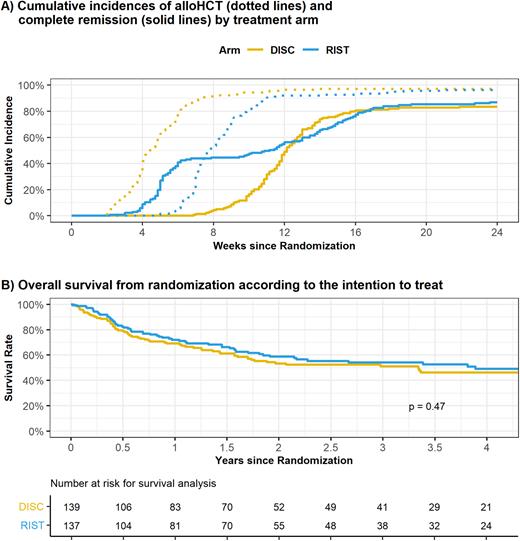
In the DISC-arm 105 of 138 pts (76%) were kept on w&w until start of sequential conditioning, while 33 pts (24%) needed disease-control measures. In the RIST-arm all pts received HAM. Sixty-two out of 134 pts (46%) achieved a CR. Five pts received a second course of intensive CT. The remaining pts proceeded to alloHCT without further attempts to induce a CR. The median time to alloHCT was 4 weeks in the DISC-arm and 8 weeks in the RIST arm. At 24 weeks from randomization 98% and 96% of pts had been transplanted in the DISC and RIST arm, respectively. Figure 1 A shows incidences of alloHCT and CR achievement in both arms. The primary endpoint CR@day56 after alloHCT was reached by 84.1% of pts in the DISC-arm and 81.3% of pts in the RIST-arm (test for non-inferiority, p=0.047). One-year leukemia-free survival from CR@day56 was 71.5% in the DISC-arm and 69.9% in the RIST-arm (z test, p=0.8).
The median follow-up from randomization is 37 months. According to the intention-to-treat, 1-year and 3-years overall survival from randomization was 69.1% (95%-CI, 60.6-76.1%) versus 71.9% (95%-CI, 63.3-78.9%) and 51.0% (95%-CI, 41.8-59.6%) versus 54.2% (95%-CI, 44.4-62.9%) in the DISC- versus RIST-arm, respectively (log-rank p=0.47) (Figure 1B).
Conclusions: This is the first randomized controlled trial, which questioned the benefit of intensive remission induction CT prior to alloHCT for pts with r/r AML. Chemotherapy with high-dose cytarabine and mitoxantrone before alloHCT did not result in a higher overall success rate and did not confer a survival advantage. Watchful waiting followed by sequential conditioning and alloHCT resulted in comparable overall CR rates and survival. These data support sequential conditioning and alloHCT without prior remission induction CT whenever a stem cell donor is readily available. Finally, these results underline the importance of facilitating alloHCT as most effective anti-leukemic therapy in patients with r/r AML and stress the need for starting donor search at diagnosis.
Disclosures
Stelljes:MSD: Consultancy, Honoraria; Jazz: Honoraria; Kite: Consultancy, Honoraria; MSD Sharp & Dohme: Consultancy; Medac: Honoraria; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria; Amgen: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Middeke:Abbvie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Bug:Pfizer: Consultancy; Jazz: Honoraria; Celgene /BMS: Consultancy, Honoraria; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria; Novartis: Consultancy. Wagner:Bristol Myers Squibb: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel Grant; Kite Gilead: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Amgen: Speakers Bureau; Medac: Other: Travel Grant; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Krause:Art-tempi: Honoraria; Kosmas: Honoraria; Abbvie: Other: Expenses. Jost:Jazz: Honoraria; BMS Celgene: Honoraria. Schubert:Alexion: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria; Roche: Other; SOBI: Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria. Röllig:BMS: Consultancy, Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria; AbbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria; Jazz: Consultancy, Honoraria; Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria; Servier: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Alakel:Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria. Steffen:Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Other: Travel/Congress Participation Support; AbbVie: Other: Travel/Congress Participation Support. Schliemann:BMS: Consultancy, Other: travel grants; Jazz: Consultancy, Research Funding; Boehringer-Ingelheim: Research Funding; Astrazeneca: Consultancy; Astellas: Consultancy; Abbvie: Consultancy, Other: travel grants; Philogen S.p.A.: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy; Roche: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy. Schetelig:Abbvie: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal